IoT Device Management: Monitor, Control & Secure Your Devices In 2024
Are you ready to unlock the true potential of your connected devices? The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing industries and everyday life, but its complexity demands robust management strategies. This article dives into the core of IoT device management, offering a comprehensive overview of its intricacies, benefits, and future trajectory.
The modern landscape is awash with connected devices, from smart home appliances and wearables to industrial sensors and autonomous vehicles. Managing these devices efficiently and securely is no longer a luxury but a necessity. The ability to remotely monitor, configure, update, and troubleshoot these devices is paramount for businesses and consumers alike. This blog serves as your guide to navigating the multifaceted world of IoT device management, providing insights into the crucial aspects that ensure optimal performance, security, and scalability.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of IoT Device Management | The centralized process of overseeing, controlling, and securing connected devices through a unified platform. This includes registration, organization, monitoring, configuration, updating, and troubleshooting. |
| Key Functions |
|
| Benefits |
|
| Challenges |
|
| Implementation Strategies |
|
| Significance of IoT Security | Securing IoT devices is paramount. It involves implementing strong authentication, encryption, and regular security audits to mitigate risks and ensure data privacy. The future of IoT hinges on robust security frameworks. |
| Future Trends |
|
| Key Technologies |
|
| Use Cases |
|
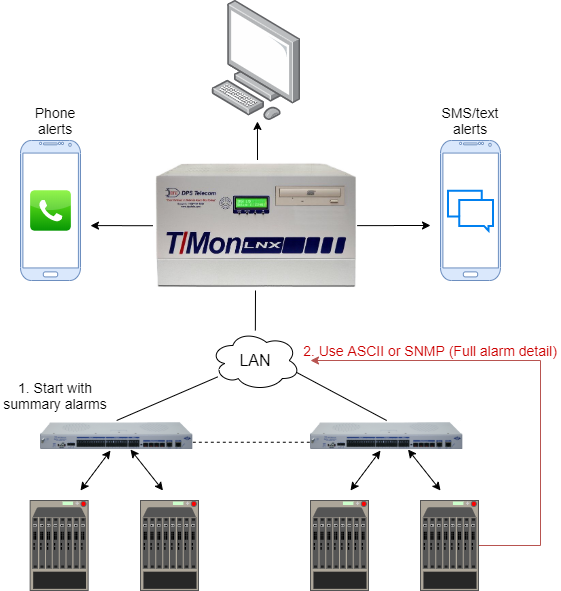
The evolution of remote device management has brought forth powerful tools and platforms, facilitating unprecedented control and insight. With solutions like RemoteIoT, businesses can remotely monitor CPU, memory, and network usage, receive alerts based on monitored IoT data, and even run batch jobs on devices. The absence of complex VPN or firewall configurations streamlines the setup process, enabling quicker deployment and ease of use. The ability to remotely access devices, review actions taken, and deploy patches from a single interface is a significant advantage in this streamlined ecosystem.
Imagine the possibilities: using a Raspberry Pi and RemoteIoT to orchestrate the workings of a smart home. The control over energy consumption and the automation of everyday routines become tangible realities, enhancing both convenience and energy efficiency. The shift toward a connected lifestyle demands a practical and reliable approach to device management.
Remote IoT device management involves the ability to monitor, configure, update, and troubleshoot connected devices through a centralized platform. This goes beyond just basic functionality; it encompasses all the essentials, including what it is, the major challenges, how to implement it effectively, and the significance of IoT security. Such comprehensive management solutions are critical for helping businesses and consumers alike derive the utmost benefits from their connected devices, whether in a driverless car or a smart city. This is why the solutions must focus on real-time data analysis and rapid response capabilities.
The use of platforms like TeamViewer underscores the necessity of advanced remote management capabilities. By integrating TeamViewer's features, users can enhance their experience and proactively maintain the health, stability, and security of their IT infrastructure. Centralized management, monitoring, tracking, and protection are all possible from a single platform, boosting IT efficiency and minimizing operational bottlenecks.
The implications for remote patient monitoring are equally transformative. Devices are particularly useful for psychologists, whose patients often require continuous prescription monitoring and adjustments. Patient wearables and monitoring systems allow healthcare professionals to manage a growing number of patients efficiently. The focus on devices needing service allows for better allocation of resources.
In the fast-paced landscape of IoT, the benefits of remote monitoring are multifaceted. It enables businesses to monitor equipment and systems in near real-time, gathering valuable insights and data to reduce downtime. This leads to informed decision-making, faster response times, and a more proactive approach to maintenance and troubleshooting. The objective is to streamline operations, optimize resource allocation, and provide enhanced services.
A survey conducted in January 2024, by Comparitech.com, polled 15,388 subscribers to gauge the RMM software usage in the workplace. Such surveys are essential in understanding the latest trends and the software tools that are being actively deployed across different business verticals. This kind of insight provides a roadmap of the software available and its application in different scenarios.
The economic factors are also noteworthy. The price for IoT device monitoring plans can start from as little as $5 per device. The various options in the market include entry-level solutions starting at $0 per month, up to 5 hosts, and others that are competitively priced from $15 per host, per month, $23 per host, per month, and $22 per host, per month. Such options make remote monitoring solutions affordable and easily accessible for businesses of all sizes. The cost-effectiveness enhances accessibility and broadens the scope of the IoT ecosystem.
In the realm of scalability and security, Google Cloud IoT Core API stands out as one of the best remote IoT APIs. It facilitates effortless integration with Googles extensive cloud infrastructure, enabling remote management and monitoring of IoT devices, which is essential for optimal performance. This integration is crucial for businesses that are planning to expand their IoT footprint. By leveraging Google Cloud, organizations can benefit from reliable and efficient services.
The management and monitoring of IoT devices in 2024 extend beyond the conventional mobile or web apps, and voice assistant integrations. Modern consumers and industrial IoT equipment operators seek an expanded range of options to engage with connected devices. The top 20 methods to manage and control IoT devices available in 2024 are indicative of this increased diversification. These methods ensure compatibility with modern systems, meeting the requirements of all end users.
The major challenges associated with IoT device management must also be addressed to guarantee optimal performance and functionality.
Security Concerns: A major challenge is safeguarding connected devices from cyberattacks. This demands strict security measures, encompassing encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
Device Diversity and Compatibility: With a vast range of devices and protocols, ensuring interoperability can be complex, often necessitating the use of standardized protocols.
Network Reliability: Reliable network connectivity is critical. Fluctuations in network stability can disrupt monitoring and control processes.
Scalability: As the volume of connected devices grows, the infrastructure must scale to handle the load efficiently, necessitating scalable solutions.
Data Management and Analysis: The vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices require efficient storage, processing, and analysis. Data management tools and analytics are essential.
To effectively implement IoT device management, these strategies must be considered:
Selecting the Right Platform: A well-suited IoT device management platform should meet specific needs, offering the necessary features for monitoring, configuration, and security.
Implementing Strong Security Protocols: Encryption, authentication, and access controls are vital to safeguard devices and data from unauthorized access.
Establishing a Centralized Dashboard: A single dashboard streamlines monitoring, configuration, and control, enabling a clear overview of all connected devices.
Automating Device Updates: Automating firmware and software updates ensures devices remain secure and functional, eliminating potential vulnerabilities.
Analyzing Data for Insights: Leveraging data analytics allows businesses to obtain actionable insights, thereby improving device performance and optimizing operational efficiency.
In this rapidly evolving technological landscape, it is crucial to consider future trends, which include:
AI-Powered Management: Employing artificial intelligence for predictive maintenance and automated device management, making maintenance schedules more proactive.
Edge Computing: Processing data closer to the devices reduces latency and improves efficiency, making real-time responses more effective.
Blockchain Integration: Enhancing security and data integrity by utilizing the immutable nature of blockchain technology, ensuring that data remains trustworthy.
Increased Automation: Automating device provisioning, configuration, and updates, saving time and resources, and optimizing workflows.
5G Connectivity: Improving connectivity and supporting a broader range of IoT applications by enhancing network capacity and reducing latency.
The core technologies that underpin IoT device management:
Remote Management Software: This type of software is purpose-built for remotely managing devices, including configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting.
Cloud Platforms: Leveraging cloud platforms for scalability, data storage, and processing capabilities, enabling businesses to handle large volumes of data.
Communication Protocols: Communication protocols, like MQTT and CoAP, facilitate seamless communication between devices and management systems, ensuring efficient data transfer.
The effective management of IoT devices plays a critical role across various sectors:
Smart Homes: Control over smart home devices, monitoring energy usage, and automating routines using technologies such as Raspberry Pi and RemoteIoT enhances convenience and energy efficiency.
Smart Cities: Optimizing urban infrastructure through real-time data analysis and control systems, contributing to efficiency, sustainability, and improved quality of life.
Industrial Automation: Monitoring and controlling industrial equipment to enhance efficiency and reduce downtime through predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring.
Healthcare: Utilizing remote patient monitoring devices, which enables the efficient management of patients and improves access to care.
Transportation: Managing and monitoring connected vehicles, including fleet management and autonomous vehicle applications.
From a technological perspective, the evolution of IoT device management is characterized by continuous advancements and innovations. The deployment of AI for predictive maintenance allows for preemptive servicing and improved device uptime. Edge computing reduces latency, while blockchain technology bolsters security and data integrity, paving the way for a more resilient ecosystem.
As we look ahead, the trends point towards enhanced automation and more seamless 5G connectivity. These advancements will be crucial for the development of new IoT applications and offer greater flexibility, responsiveness, and integration capabilities. The future will bring about an era where IoT devices are managed with unprecedented efficiency and control, enhancing user experiences and business outcomes. The emphasis on efficiency and security, driven by these trends, will define the landscape of IoT management going forward.
The journey toward effective IoT device management encompasses several key steps, from selecting the correct platform to implementing robust security measures. Through the integration of powerful tools, the advantages of remote monitoring are clear, offering businesses and consumers the capabilities to maximize the potential of their connected devices. The ongoing evolution within the IoT landscape underscores the importance of a proactive approach to device management, thereby ensuring that you will be well-equipped for whatever the future holds.

Remote Monitoring of IoT Devices Implementations AWS Solutions

What Is Remote Monitoring Iot Enabled Remote Monitori vrogue.co
Comprehensive Guide To RemoteIoT Monitoring Devices Examples